Hash based predictive algorithm for typing
Project Details
- Project Type: Programmation in C
- Tools: C, git
- Duration: 2 weeks
- Team: Duo project with Antoine Banchet
Introduction
The goal of this project is to develop a predictive typing software in C. The software will predict the next word based on the first characters typed by the user. The software will use a hash table to store the words and their frequency in a text file. The software will be able to predict the next word based on the frequency of the words in the text file.
Project Overview
The project involves:
Developing in C
Using a hash table to store the words and their frequency in a file
Predicting the next word based on the frequency of the words in the text file in real time
General Description of the Project
The project focuses on developing a predictive text algorithm using a trie data structure. This trie has nodes with 27 children: 26 for each letter of the alphabet and one for special characters, represented by the symbol #. The algorithm works by traversing the trie from the root, following the letters of the input word sequentially. Nodes with a weight of 0 indicate that the traversal has not reached the end of a word, while nodes with a positive weight denote the end of a word and its significance. This structure enables the predictive text algorithm to suggest relevant words to users in real-time based on their input.
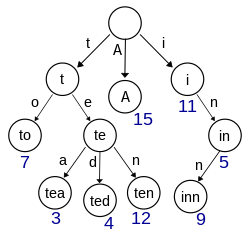
Figure 1: Illustration demonstrating how a trie sort can aid in identifying which letters are more frequently used in known words.
Libraries
| |
The library hash.h implements a hash table for storing and searching words in nearly constant time. It uses a linked list to handle collisions.
| |
The library trie.h implements a prefix tree (trie) for storing and searching words. Tries are also known as prefix trees.
| |
The trie structure enables a predictive text algorithm. Each node in this tree contains 27 children: 26 for each letter of the alphabet and the 27th for managing special characters, represented by the symbol #.
The algorithm operates by traversing the trie from the root, following each letter of the input word one by one. If a node has a weight of 0, it indicates that it’s not the end of a word. Conversely, if the node’s weight is greater than 0, it signifies the end of a word and its importance.
This trie structure allows the predictive text algorithm to suggest relevant words to the user in real-time, based on the letters they input.
Description of necessary functions
| |
This function create_node creates a new node in a trie tree. It takes a character “letter” as input, which will be stored in the newly created node. The function initializes all children to NULL and sets the weight to 0.
| |
The add_word function traverses the word character by character and creates nodes for each letter of the word. If a node for that letter does not yet exist, it is created and placed in the “child” array of the current node. The “weight” field of the last created node is then incremented to indicate that this node marks the end of a word and to assign its weight.
| |
This function reads a text file and adds each word to the trie.
| |
The suggest_words function is central to the program. It takes a prefix and a trie tree containing words as inputs. It searches for all words in the dictionary that start with this prefix by traversing the trie tree from the root to the last node corresponding to the prefix’s last letter. Then, it uses a search function to find all words following this prefix and stores them in a linked list, which it sorts before returning.
| |
These functions allow saving and loading the trie structure from a binary file.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the predictive typing software developed in C is a powerful tool that can predict the next word based on the frequency of words in a text file. The software uses a hash table to store the words and their frequency and a trie data structure to predict the next word based on the user’s input. The software is efficient and can predict the next word in real time.
However, today these types of software are not used anymore because of the power of modern computers and the use of machine learning.